
Private 5G Network Ecosystem Partners
Deploying a private 5G network is a complex undertaking that presents a steep learning curve for even the most capable IT teams. Enterprise decision-makers need to work with partners who can help them climb this learning curve and realize private 5G’s full potential. Here I present an overview of the private 5G network ecosystem and outline the roles of the types of companies that enterprises can partner with to achieve successful outcomes.
I’ll start by grouping players in the private 5G network ecosystem into three broad categories:
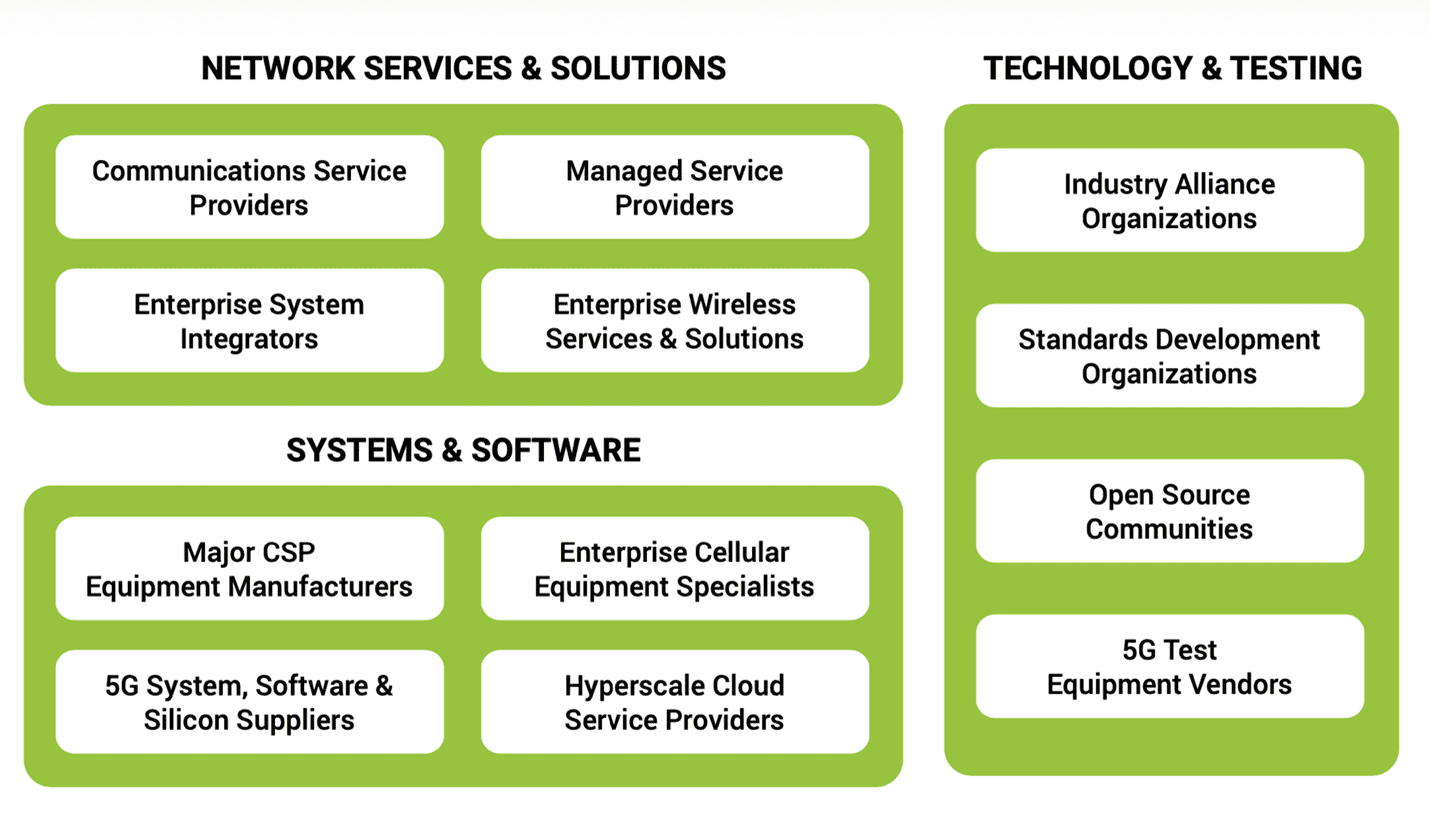
This post will concentrate on players in the two categories on the left-hand side of the diagram. I’ll conclude with a few comments about key players in technology and testing but will focus on that category in a future post.
With so many alternatives for private 5G network services and solutions providers, how do enterprise decision-makers choose the right partners? Just as private 5G networks are not one-size-fits-all, there is no one type of partner that is right for every enterprise. Choosing partners depends on many factors, such as the industry vertical, specific use cases, the deployment model, access to spectrum, coverage requirements and operational scale.
Enterprise System Integrators
On-premise private 5G deployments require integrating complex cellular radio systems and software into enterprise IT operations to provide connectivity for innovative use cases supporting new types of devices and applications. Enterprises will want to partner with system integrators and/or industry-specific solutions providers to conduct the initial analysis and evaluation needed to identify and quantify the business benefits of deploying private 5G, including defining the functional requirements for the initial set of use cases that justify the decision to deploy. Ideally, system integrators will have prior experience implementing these use cases in private 5G (or possibly LTE) networks.
Leading system integrators offer a broad range of capabilities, including teams experienced in network engineering, product integration, interoperability testing, installation and network operations. Integrators will often play a key role in pulling together all of the elements in the broader private 5G ecosystem, including 5G devices, application software, edge computing platforms and cloud services. Kyndryl, Microland, Tata and WWT are just a few examples of leading system integrators with private 5G practices.
Communications Service Providers (CSPs)
CSPs are leading players in private 5G, with mobile operators building on years of experience in private LTE networks. CSPs have enterprise-focused managed services business units that are responsible for private 5G. The three big U.S. mobile operators, AT&T, T-Mobile and Verizon, each offer private 5G managed services. Other CSPs active in the U.S. market include NTT, Comcast, Cox, and new 5G network operator Dish Network.
Major CSP Equipment Manufacturers
Leading equipment manufacturers such as Ericsson and Nokia supply their CSP customers with systems and software for private 5G, but they also sell private 5G networks to enterprises directly, offering a range of managed services, either directly or via partners.
Managed Service Providers (MSPs)
This is a very broad category of companies that provide services encompassing network planning and design, sourcing equipment, installation and network operations. MSPs tend to work from a playbook of proven reference architectures and solutions that are pre-integrated and validated for specific use cases.
MSPs for managed WiFi and managed SD-WAN services are moving into private 5G, leveraging their position in these adjacent markets. Private 5G has also attracted the interest of big tech players such as AWS, Cisco and VMware, who are offering private 5G as a managed service. This trend will continue, as well-positioned players capitalize on this growing market opportunity to augment their core business.
Enterprise Wireless Services and Solutions
Companies that specialize in fully-managed, end-to-end enterprise wireless services and solutions are moving into private 5G to complement their current business in WiFi and/or private LTE. Examples of players in this category include Betacom, Boingo and Kajeet.
5G System, Software & Silicon Suppliers
Turning our attention to network systems and software suppliers, three building blocks serve as the foundation for private 5G networks:
Merchant Silicon
Chip makers provide the enabling core technologies for 5G radio networks. RF transceiver and 5G baseband processing functions are embedded in merchant silicon implemented in RFICs, ASICs and FPGAs. 5G chip makers include Qualcomm, Intel, AMD, Analog Devices and Samsung, among many others.
vRAN Infrastructure
The vast majority of LTE and 5G base station hardware and software supplied by leading CSP equipment manufacturers is based on vertically integrated, vendor-proprietary designs incorporating custom and merchant silicon. This type of equipment will continue to be widely deployed in both public and private 5G networks, however, these manufacturers are moving to disaggregated, virtualized RAN infrastructure, generically referred to as vRAN.
Open RAN is an emerging standards-based vRAN architecture that is horizontally and vertically disaggregated, specifying open interfaces between constituent components. Virtualized Open RAN software functions are cloud-native and designed to run on common server platforms. Leading IT infrastructure vendors such as Dell, HPE, IBM, Red Hat and VMware are all active players in Open RAN, which is well-suited for private 5G implementations since it is compatible with the new generation of cloud-native IT infrastructure.
5G Core Functions
The 5G Core is comprised of software functions that control the operation of the 5G network and includes the User Plane Function (UPF) for switching IP packets through the network. Enterprises have several options for deploying a private network 5G Core.
Private 5G networks managed by a CSP can be controlled by the 5G Core in the mobile network operator’s network, although the UPF might have to be located on-site, depending on the performance and security requirements. The 5G Core could also be hosted by a CSP equipment manufacturer or hyperscale cloud provider, with the UPF located either on-site or at the cloud edge. Alternatively, the 5G Core could reside in an on-site data center. Druid Software and Athonet (recently acquired by HPE) are vendors that specialize in 5G Core software for on-premise deployments.
Enterprise Wireless Equipment Vendors
While CSP equipment manufacturers have expansive product portfolios and partnerships that enable them to serve as a one-stop-shop for private 5G infrastructure, another alternative is vendors that specialize in enterprise-grade wireless equipment. 5G “small cells” are a cost-effective solution for in-building and campus area coverage. There are many alternatives, with a wide range of vendors manufacturing radio systems well-suited for private 5G. Examples include Airspan, Celona Networks, Cradlepoint (acquired by Ericsson), JMA Wireless, GXC and Mavenir.
Hyperscale Cloud Providers
Hyperscale cloud providers AWS, Azure and Google can simplify on-premise private 5G deployments by integrating and managing private 5G network software in the cloud. Cloud-based solutions can streamline the process of spinning up new sites, enabling enterprises to rapidly scale as needed. Cloud providers also have the capability to deploy 5G software in an on-site data center, offering enterprises the best of both worlds.
5G Test Equipment Vendors
In closing, I want to call out the vital role of test equipment vendors in the private 5G network lifecycle, which spans initial lab testing and proof-of-concept demos to field trials and full-scale operations. Cellular networks require sophisticated equipment for testing and assurance of complex RF and baseband processing functions. Private 5G operators will be tasked with meeting stringent SLAs, so the network should be fully instrumented with active assurance capabilities for continuously monitoring radio network performance and reliability. Leading vendors in this category include Anritsu, Keysight, NETSCOUT, Spirent and VIAVI.
I have covered a lot of ground here so I will defer further description of the technology and testing category for a future post, but for now be aware that there is a wide array of ecosystem players who are collaborating to accelerate the adoption of private 5G networks by educating the market, advocating for 5G spectrum, surmounting technical obstacles, conducting multi-vendor interoperability tests, developing reference architectures, working on open source projects and defining standards for 5G networks.
Please note that all of my private 5G blog posts in this series can be found here, and you can subscribe to this blog here.


